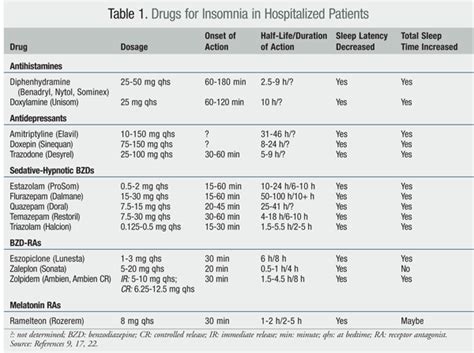
Best Insomnia Drugs: A Complete Guide to MedicationsHey there, guys! Ever found yourself staring at the ceiling at 3 AM, wishing you could just
turn off your brain
and get some much-needed shut-eye? If so, you’re definitely not alone.
Insomnia
is a super common and incredibly frustrating problem that affects millions of people worldwide. It’s not just about feeling tired; long-term sleep deprivation can seriously mess with your health, mood, and overall quality of life. That’s why many of us, at some point, start looking into
insomnia drugs
or
medications to help us sleep
. Understanding the different
insomnia drug names
and how they work can feel a bit like navigating a complex maze, right? But don’t you worry, because this comprehensive guide is here to shed some light on the subject, breaking down everything you need to know about
sleep medications
in a friendly, easy-to-understand way. We’re going to dive deep into the world of
insomnia treatment options
, focusing specifically on the
various types of insomnia drugs
available, what their
names
are, and what you should consider before taking them.When we talk about
insomnia drugs
, it’s important to remember that they aren’t a one-size-fits-all solution. What works wonders for one person might not be the best fit for another, and sometimes, a
combination of approaches
is needed. Our goal here is to empower you with knowledge, making sure you understand the
different classes of sleep medications
, their
benefits
,
potential side effects
, and
how to discuss them with your doctor
. We’ll cover everything from the well-known
benzodiazepines
and
Z-drugs
to newer, more targeted treatments like
orexin receptor antagonists
and even some
over-the-counter options
or
off-label prescriptions
that doctors sometimes use. You’ll learn about
specific drug names
like zolpidem, temazepam, ramelteon, and suvorexant, demystifying the jargon so you can have a more informed conversation with your healthcare provider. This isn’t just about listing
insomnia medication names
; it’s about understanding the
science behind sleep
, how these
drugs interact with your body
, and ultimately, helping you find a path toward better, more restful nights. So, grab a comfy pillow, maybe a warm drink, and let’s get into the nitty-gritty of
insomnia drug treatments
and how they can potentially help you reclaim your sleep. Remember, guys, a good night’s sleep isn’t a luxury; it’s a necessity for your well-being, and exploring
effective insomnia solutions
is a crucial step in achieving it. This article is your ultimate resource for decoding the world of
insomnia pharmaceuticals
.## Understanding Insomnia and Why We Need
Drugs for Sleep**Insomnia
isn’t just a bad night’s sleep; it’s a persistent
sleep disorder
that can truly wreak havoc on your life, guys. We’re talking about difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early and being unable to get back to sleep. This isn’t just a temporary inconvenience; for many, it’s a chronic struggle, defined as happening at least three nights a week for three months or more. When you’re constantly battling
sleep deprivation
, it impacts everything: your energy levels plummet, your concentration becomes fuzzy, your mood swings become more frequent, and your overall physical health can take a serious hit. Think about it – your body and brain rely on sleep to repair, consolidate memories, and regulate hormones. When that process is disrupted, you’re not just tired; you’re operating at a significant disadvantage.
Chronic insomnia
can lead to an increased risk of accidents, impaired work performance, relationship problems, and even serious health issues like high blood pressure, diabetes, and depression. It’s a vicious cycle where anxiety about not sleeping can actually make it harder to sleep. The causes of
insomnia
are incredibly varied, spanning from stress, anxiety, and depression to underlying medical conditions, certain medications, poor
sleep hygiene
, and even lifestyle choices like excessive caffeine or alcohol consumption. Sometimes, it’s a combination of these factors, making it a really complex puzzle to solve.For many people, trying to fix
insomnia
often starts with lifestyle adjustments. We’re talking about things like setting a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, avoiding screens before bed, and cutting back on stimulants. These
behavioral therapies
, especially Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I), are often recommended as first-line treatments and can be incredibly effective in the long run. However, for some folks, these changes alone aren’t enough, or the
insomnia
is so severe that they need a more immediate solution to break the cycle of sleep deprivation. This is where
drugs for sleep
come into play. While they’re generally not considered a permanent fix – the goal is often to use them short-term to reset your sleep patterns while you work on underlying issues –
insomnia medications
can offer a crucial lifeline. They can provide the immediate relief needed to catch up on sleep, improve daily functioning, and give you the mental space to implement long-term
sleep strategies
. It’s about finding that balance between symptomatic relief and addressing the root causes. Choosing to use
insomnia drugs
is a decision that should always be made in consultation with a healthcare professional, who can assess your specific situation, rule out other conditions, and help you understand the
risks and benefits
of different
medication options
. They can guide you through the maze of
insomnia drug names
and help you select the most appropriate
sleep aid
for your unique needs, ensuring it complements rather than conflicts with your overall health. So, while we champion natural and behavioral approaches, we also recognize the vital role that
pharmacological interventions
can play in helping people overcome the debilitating effects of
insomnia
and reclaim their nights. Understanding
why and when
these
sleep medications
are used is the first step in making an informed choice about your
insomnia treatment journey
.## Types of
Insomnia Drugs
: Exploring *Medication Names*Alright, let’s get to the good stuff, guys – understanding the actual
types of insomnia drugs
and their
medication names
. It’s a pretty diverse landscape out there, and each class of
sleep medication
works a bit differently, targeting various pathways in your brain to help you achieve that elusive slumber. It’s not just about one pill for every problem; it’s about finding the right key for your particular sleep lock. We’ll explore the main categories, giving you the lowdown on how they function, what they’re commonly prescribed for, and what you should keep an eye out for. Remember, this information is for educational purposes, and you should always chat with your doctor before starting or changing any
insomnia drug treatment
.### Benzodiazepines: *Common Sleep Medications*When we talk about traditional
sleep medications
,
benzodiazepines
are often among the first
insomnia drug names
that come to mind. These powerful compounds have been around for a while and are known for their sedative, anxiolytic (anti-anxiety), muscle-relaxant, and anticonvulsant properties. How do they work, you ask? Well, they enhance the effect of a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in your brain. GABA is your brain’s primary inhibitory neurotransmitter, meaning it slows down brain activity, leading to a calming and sleep-inducing effect.
Common benzodiazepine drug names
prescribed for
insomnia
include
temazepam
(Restoril),
triazolam
(Halcion),
estazolam
(ProSom), and
flurazepam
(Dalmane). Each of these has a slightly different duration of action; for example, triazolam is very short-acting, often used for difficulty falling asleep, while temazepam is intermediate-acting, helping with both falling and staying asleep.While
benzodiazepines
can be incredibly effective for short-term
insomnia relief
, they come with some significant caveats. One of the biggest concerns is the risk of
dependence and withdrawal symptoms
if used for extended periods. Your body can get used to them, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effect, which is what we call tolerance. Stopping them abruptly after prolonged use can lead to rebound insomnia, where your sleep actually gets worse than before, along with other unpleasant withdrawal effects like anxiety, agitation, and even seizures in severe cases. Another important consideration is their
side effect profile
. Common
side effects of insomnia drugs
in this class can include daytime drowsiness, dizziness, impaired coordination, and memory problems (amnesia). For older adults, the risks are even higher, as they can significantly increase the chance of falls and cognitive impairment. Due to these risks, doctors typically prescribe
benzodiazepines
for very
short-term insomnia treatment
, usually just a few weeks, to help you get over a rough patch while you implement other
sleep-improving strategies
. They are generally not recommended for chronic
insomnia
unless other treatments have failed and the benefits clearly outweigh the risks, and even then, under strict medical supervision. Always remember, guys, never share these
insomnia medications
or use them without a doctor’s prescription, as they are controlled substances due to their potential for abuse. Understanding these
benzodiazepine drug names
and their implications is crucial for safe and effective
sleep management
.### Z-Drugs: *Newer Insomnia Medications*Moving on from benzodiazepines, let’s talk about the
Z-drugs
. These are often seen as the
newer insomnia medications
or “non-benzodiazepine hypnotics,” and they’ve gained popularity because they tend to have a slightly different chemical structure and work a bit more selectively than traditional benzos, specifically targeting certain GABA receptors involved in sleep. The main
Z-drug names
you’ll encounter are
zolpidem
(Ambien, Edluar, Zolpimist),
eszopiclone
(Lunesta), and
zaleplon
(Sonata). These
sleep aids
are designed to help you fall asleep faster and/or stay asleep longer, depending on the specific drug and its formulation. Zolpidem, for instance, is well-known for helping people initiate sleep and comes in different forms, including extended-release versions for maintaining sleep. Eszopiclone is notable for being approved for
long-term use
(though this is still debated and often approached with caution), helping with both sleep onset and maintenance. Zaleplon, on the other hand, is a very short-acting Z-drug, ideal for those who wake up in the middle of the night and need help getting back to sleep, as it’s less likely to cause next-day drowsiness if taken at least four hours before waking.So, how do these
Z-drugs
differ from benzodiazepines in practice? While they also work on GABA receptors, their more selective action theoretically means a lower risk of certain
side effects
, such as muscle relaxation or anti-anxiety effects that aren’t directly related to sleep. However, it’s really important to understand that
Z-drugs
are not without their own
potential side effects
and risks. Just like benzodiazepines, they can cause daytime drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired coordination. But perhaps the most talked-about
side effects of these insomnia drugs
are the “sleep behaviors” – things like sleepwalking, sleep-driving, making phone calls, or even preparing and eating food, all while not fully awake and having no memory of it afterward. These paradoxical effects, though rare, can be serious and are a major reason why
Z-drugs
should always be taken exactly as prescribed, ideally right before bed, and only when you know you have a full 7-8 hours available for sleep. The risk of
dependence and withdrawal
is still present, especially with prolonged use, though some studies suggest it might be slightly lower than with traditional benzos. Doctors often prescribe
Z-drugs
for short-term
insomnia treatment
, helping patients get their sleep schedule back on track. They are generally considered effective
sleep medications
for improving
sleep latency
(how long it takes to fall asleep) and
sleep maintenance
. Again, guys, open communication with your doctor about your sleep patterns, any
side effects
you experience, and your overall health is key to safely and effectively using these
insomnia drugs
. Don’t forget, these are powerful tools, and responsible use is paramount to harnessing their benefits without falling prey to their downsides.### Melatonin Receptor Agonists: *Natural-ish Sleep Aids*If you’re looking for
insomnia drugs
that work a bit differently and might feel a bit more “natural” in their approach, then
melatonin receptor agonists
could be a topic of discussion with your doctor. These
sleep aids
don’t work by broadly depressing the central nervous system like benzos or Z-drugs. Instead, they mimic the action of melatonin, a hormone naturally produced by your brain’s pineal gland, which plays a crucial role in regulating your body’s
sleep-wake cycle
or circadian rhythm. When darkness falls, your brain releases melatonin, signaling to your body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep.
Melatonin receptor agonists
essentially give your body a little extra nudge in that direction. The primary
melatonin receptor agonist drug name
currently available for
insomnia treatment
is
ramelteon
(Rozerem). Unlike synthetic melatonin supplements, which are available over-the-counter and vary in potency and regulation, ramelteon is a prescription medication that acts specifically on two types of melatonin receptors (MT1 and MT2) in the brain, which are involved in promoting sleep and synchronizing circadian rhythms. This makes it a more targeted and potent option than many OTC melatonin products.One of the significant advantages of
ramelteon
and other
melatonin receptor agonists
is their low potential for abuse and dependence, making them a more attractive option for people who are concerned about those issues with other
insomnia medications
. Because they don’t act on GABA receptors, they typically don’t cause the classic sedative
side effects
like significant daytime drowsiness or the “hangover” feeling often associated with benzos or Z-drugs. They also don’t seem to cause the peculiar sleep behaviors sometimes seen with Z-drugs. However, that doesn’t mean they’re entirely free of
side effects
. Some common, though usually mild,
side effects of this insomnia drug
can include dizziness, nausea, and fatigue. It’s also important to note that because
ramelteon
works by adjusting your circadian rhythm, it might take a bit longer to feel its effects, and it’s most effective when taken consistently at the same time each night, about 30 minutes before bedtime. It’s particularly useful for individuals who have difficulty falling asleep (sleep onset insomnia) and those whose
insomnia
is linked to circadian rhythm disruptions, such as shift workers or people with jet lag (though it’s not specifically approved for jet lag, its mechanism makes it relevant). While it generally has fewer drug-drug interactions compared to other
insomnia drugs
, it’s still crucial to discuss all your current medications with your doctor to ensure safety. For those seeking a
sleep aid
that supports the body’s natural processes rather than forcibly inducing sleep,
ramelteon
represents a compelling
insomnia treatment option
. It emphasizes the importance of understanding the underlying cause of your
insomnia
to choose the most appropriate
medication name
and approach.### Orexin Receptor Antagonists: *Targeted Sleep Solutions*Alright, let’s talk about some of the newer, really innovative
insomnia drugs
on the block:
orexin receptor antagonists
. These
medications for sleep
represent a pretty fascinating shift in how we approach
insomnia treatment
because instead of directly promoting sleep by dampening brain activity, they work by blocking wakefulness. Think of it this way, guys: traditional sleep aids hit the “off” switch, while orexin antagonists essentially disable the “on” switch for wakefulness. This unique mechanism targets the orexin signaling system in the brain, which plays a central role in promoting wakefulness and keeping us alert. By blocking the receptors for orexin (also known as hypocretin), these
sleep drugs
reduce the “drive to wake up,” allowing your body’s natural sleep processes to take over. This is a big deal because it means they’re not simply sedating you; they’re helping to rebalance your sleep-wake cycle by reducing the signals that keep you awake. The main
orexin receptor antagonist drug names
currently available include
suvorexant
(Belsomra),
lemborexant
(Dayvigo), and
daridorexant
(Quviviq). Each of these has slightly different pharmacological profiles, but they all share this core mechanism of action.These
insomnia drugs
are typically prescribed for people who have difficulty falling asleep
and
staying asleep. Because they work by actively blocking wakefulness signals, rather than inducing generalized sedation, they are thought to offer a more “physiological” approach to
insomnia treatment
. This also translates to a potentially different
side effect profile
compared to older
sleep medications
. While generally well-tolerated,
common side effects
can include drowsiness, headache, and dizziness. A key point of discussion with your doctor, especially with
suvorexant
and
lemborexant
, is the potential for next-day drowsiness or “sleepiness.” Because these drugs block wakefulness signals, you need to ensure you have a full 7-8 hours available for sleep after taking them, otherwise, you might feel groggy the next morning.
Daridorexant
, being the newest of the trio, was specifically developed to minimize next-day effects while still effectively promoting sleep. The good news is that
orexin receptor antagonists
generally have a low risk of physical dependence or rebound
insomnia
upon discontinuation, which is a major advantage for people concerned about long-term use. However, like all
insomnia drugs
, they can still be associated with complex sleep behaviors, so it’s vital to use them as prescribed and discuss any unusual experiences with your healthcare provider. For individuals whose
insomnia
is driven by an overactive wakefulness system, or for those seeking
sleep medications
with a lower dependence risk, these
orexin drug names
represent a powerful and modern
targeted sleep solution
. They highlight the continuous advancements in
insomnia pharmacology
aimed at improving
sleep quality
and duration for millions.### Antidepressants and Antihistamines Used Off-Label for *Sleep*Beyond the dedicated
insomnia drugs
we’ve discussed, it’s pretty common, guys, for doctors to prescribe other classes of medications “off-label” to help with sleep. “Off-label” simply means the drug is approved by regulatory bodies for one condition (like depression or allergies) but is being used for another (like
insomnia
) based on clinical experience and evidence, even if it’s not officially in the drug’s approved indications. This practice is totally legal and can be very effective, especially when a patient has co-occurring conditions. The two main categories here are certain
antidepressants
and
antihistamines
.Let’s start with
antidepressants used for sleep
. Some antidepressants, particularly the older tricyclic antidepressants and certain newer ones, have sedating
side effects
that can be leveraged to help with
insomnia
. The most commonly prescribed
antidepressant drug name
for sleep is
trazodone
(Desyrel). While it’s primarily an antidepressant, at lower doses, it’s often very effective in inducing sleep with a relatively low risk of dependence. It works by affecting serotonin in the brain and has an alpha-adrenergic blocking effect, which contributes to its sedative properties.
Side effects of trazodone
can include daytime drowsiness, dizziness, and dry mouth. Another antidepressant sometimes used off-label is
doxepin
(Silenor), particularly in low doses, which is actually specifically approved for
insomnia
characterized by difficulty staying asleep. It’s a tricyclic antidepressant but acts more like an antihistamine at low doses to block histamine receptors, promoting sleep without the typical antidepressant effects. Other antidepressants like mirtazapine (Remeron) can also be sedating, particularly at lower doses, due to their antihistamine and alpha-adrenergic blocking effects. These
insomnia drugs
can be particularly beneficial for individuals whose
insomnia
is linked to underlying depression or anxiety, offering a dual benefit.Then we have
antihistamines
. While you might think of them for allergies, certain first-generation
antihistamines
are known for causing significant drowsiness, which is why they are often found in
over-the-counter sleep aids
. The most common
antihistamine drug names
used for sleep are
diphenhydramine
(found in Benadryl, ZzzQuil, and many generic sleep aids) and
doxylamine
(Unisom). These drugs work by blocking histamine H1 receptors in the brain, leading to sedation. They can be helpful for occasional
insomnia
, but they are generally not recommended for chronic use. Why not? Well, for starters, the
sedative effects
can persist into the next day, leading to grogginess and impaired performance. More importantly, especially in older adults, they carry a higher risk of anticholinergic
side effects
like dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, and cognitive impairment. Long-term use of anticholinergic
insomnia drugs
has even been linked to an increased risk of dementia. So, while readily available, these are generally considered short-term solutions. It’s crucial, guys, to discuss with your doctor if you’re regularly relying on these
off-label insomnia drugs
or
OTC sleep aids
, as there might be more appropriate and safer long-term
insomnia treatment options
available. The key takeaway here is that while these medications can be useful, their use for sleep is often secondary to their primary indication, and their
side effect profiles
need careful consideration. Always consult a healthcare professional to ensure these
sleep aids
are right for you and don’t interact negatively with other medications you might be taking.## Important Considerations When Taking *Insomnia Medication*Okay, guys, so we’ve covered a whole bunch of
insomnia drug names
and how they work. That’s a huge step towards understanding your options. But knowing the
medication names
is just one piece of the puzzle. What’s equally, if not more, important are the
important considerations when taking insomnia medication
. Seriously, this part is crucial for your safety and for making sure you get the most benefit out of any
sleep aid
without falling into common pitfalls. Taking
insomnia drugs
isn’t like taking a vitamin; these are powerful pharmaceuticals that interact with your body in complex ways, and responsible use is absolutely paramount. First and foremost,
always consult your doctor or a qualified healthcare professional
before starting any new
insomnia medication
, changing your dose, or stopping an existing one. They can assess your overall health, review your medical history, including any existing conditions like sleep apnea or kidney/liver issues, and consider all other medications you’re currently taking. This is vital to prevent dangerous
drug interactions
and to ensure the chosen
insomnia drug
is safe and appropriate for your specific situation. Self-medicating with prescription
sleep drugs
or combining them with alcohol or other sedatives can be extremely risky, leading to severe drowsiness, respiratory depression, or even overdose.Beyond the initial consultation, let’s talk about
side effects
. Every
insomnia drug
has them, and while we’ve touched on some specific ones for each class, it’s essential to be vigilant. Common
side effects
across many
sleep medications
include daytime drowsiness, dizziness, lightheadedness, and impaired coordination. These can increase your risk of falls, especially in older adults, and can make activities like driving or operating machinery dangerous. If you experience unusual or severe
side effects
, such as paradoxical agitation, hallucinations, or complex sleep behaviors (sleepwalking, sleep-driving, etc., without memory), you need to contact your doctor immediately. Dosage is another critical factor. Always take the
lowest effective dose
for the
shortest duration
necessary. The goal of
insomnia treatment
with medication is often to break the cycle of sleep deprivation and give you a chance to implement better
sleep hygiene
practices, not to become a permanent crutch. Long-term use of many
insomnia drugs
can lead to tolerance, dependence, and withdrawal symptoms when stopped. If your
insomnia
doesn’t improve after a few weeks on medication, or if you feel you’re developing a tolerance, it’s time to revisit your doctor to re-evaluate your
treatment plan
. They might suggest trying a different
insomnia drug name
, adjusting the dose, or exploring non-pharmacological approaches like CBT-I more intensely.Finally, and perhaps most importantly,
insomnia medication
should never be viewed in isolation. It’s almost always most effective when combined with excellent
sleep hygiene
and other lifestyle changes. Think of the drug as a helping hand, not a magic bullet. Things like maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, ensuring your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool, avoiding caffeine and heavy meals close to bedtime, and getting regular exercise are all fundamental to long-term
sleep success
.
Insomnia drugs
can give you the temporary relief you need to make these changes effectively. Without addressing the underlying habits and issues, the
insomnia
is likely to return once the medication is stopped. So, guys, be proactive! Educate yourself, be open and honest with your doctor, closely monitor your body’s response to any
insomnia drug
, and commit to holistic
sleep improvement strategies
. Your journey to better sleep is a partnership between you and your healthcare provider, where understanding
insomnia drug names
and their responsible use is a cornerstone of your success.So there you have it, guys – a deep dive into the fascinating, sometimes confusing, world of
insomnia drugs
and
sleep medications
. We’ve journeyed through the various
types of insomnia drugs
, from the well-established
benzodiazepines
and
Z-drugs
to the more targeted
melatonin receptor agonists
and
orexin receptor antagonists
, and even touched upon
off-label options
like certain
antidepressants
and
antihistamines
. Understanding the
names
like zolpidem, temazepam, ramelteon, and suvorexant, and knowing how each class works to influence your
sleep-wake cycle
, is empowering. It helps you grasp that
insomnia treatment
is nuanced and often personalized. We’ve emphasized that while these
insomnia drugs
can be incredibly beneficial in providing much-needed relief from persistent
sleep deprivation
, they are not without their
side effects
and risks, including the potential for dependence or the infamous “sleep behaviors.” The core message throughout all this, guys, is the absolute importance of professional guidance. Never, ever, embark on an
insomnia drug regimen
without a thorough discussion with your doctor. They are your best resource for navigating the complex landscape of
insomnia medications
, helping you weigh the
benefits against the risks
, identifying
potential drug interactions
, and ensuring you choose the
most appropriate sleep aid
for your unique health profile and
insomnia type
.Remember,
insomnia medication
is often most effective when used as part of a broader
insomnia treatment strategy
. This means pairing it with robust
sleep hygiene
practices, addressing any underlying medical or psychological conditions, and potentially engaging in behavioral therapies like CBT-I. The goal isn’t just to pop a pill; it’s to cultivate sustainable, healthy sleep patterns that will serve you well in the long run. By arming yourself with knowledge about
insomnia drug names
, their mechanisms, and the crucial considerations for safe use, you’re taking a powerful step toward reclaiming your nights and, consequently, improving your overall quality of life. Don’t let
insomnia
win, guys. Be informed, be proactive, and work with your healthcare team to find the best path to restful, rejuvenating sleep. Sweet dreams!

